Warning: Undefined variable $ext in /www/wwwroot/gkfeed.com/public_html/wp-content/plugins/show-hidecollapse-expand/bg_show_hide.php on line 281
Warning: Undefined variable $ext in /www/wwwroot/gkfeed.com/public_html/wp-content/plugins/show-hidecollapse-expand/bg_show_hide.php on line 281
Warning: Undefined variable $ext in /www/wwwroot/gkfeed.com/public_html/wp-content/plugins/show-hidecollapse-expand/bg_show_hide.php on line 281
4. A cell biologist is studying the role of ribonucleoproteins in normal cellular function. He prepares a cell extract using a specific cell type obtained from a 73-year-old man. Ribonucleoproteins are separated and purified from the cell extract for structural and functional analyses. These cells are found to express higher amounts of a particular protein in comparison to other cell types. This protein has reverse transcriptase activity that functions to add TTAGGG repeats to the 3′ end of chromosomes. Which of the following cell types was most likely studied in this experiment?
A. Epidermal basal cells
B. Erythrocytes
C. Myocardial cells
D. Neurons
E. Pancreatic β cells
5. A 9-month-old boy is brought to the clinic for a routine follow-up. His mother is concerned because the patient is not yet able to sit up unsupported. He was born at term and has had muscle weakness since birth. Vital signs are normal. The patient is alert but has diminished tone. Examination shows a prominent forehead with a depressed nasal bridge. Eye examination shows epicanthal folds. Analysis of lysosomal acid hydrolases shows an increased concentration within the serum and a decreased level within the cultured skin fibroblast cells. This patient most likely has a defect in which of the following steps of enzyme production?
A. DNA methylation
B. Posttranslational modification
C. Protein folding
D. Splicing
E. Translation
6. An infant born to a 34-year-old woman has a flat facial profile, prominent epicanthal folds, and a holosystolic murmur heard loudest at the left sternal border. Karyotype analysis is consistent with trisomy 21. Maternal and paternal karyotypes are normal. A restriction fragment length polymorphism (R FLP) analysis is conducted to determine the parental origin of the extra chromosome. DNA samples from the child, mother, and father are obtained and the DNA is fragmented with a restriction enzyme. The fragments are then sorted by size using the Southern blot technique. Labeling is done using a probe that binds to a specific DNA sequence close to the centromere of chromosome 21 . RFLP analysis for the child, mother, and father is shown below.
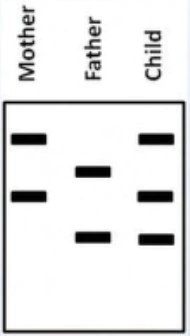
In which of the following meiosis events did the nondisjunction most likely occur?
A. Maternal meiosis I
B. Maternal meiosis II
C. Paternal meiosis I
D. Paternal meiosis II
Warning: Undefined variable $in_same_cat in /www/wwwroot/gkfeed.com/public_html/wp-content/plugins/EXP.GKFEED.COM/function.php on line 27
Warning: Undefined variable $excluded_categories in /www/wwwroot/gkfeed.com/public_html/wp-content/plugins/EXP.GKFEED.COM/function.php on line 27