Warning: Undefined variable $ext in /www/wwwroot/gkfeed.com/public_html/wp-content/plugins/show-hidecollapse-expand/bg_show_hide.php on line 281
Warning: Undefined variable $ext in /www/wwwroot/gkfeed.com/public_html/wp-content/plugins/show-hidecollapse-expand/bg_show_hide.php on line 281
Warning: Undefined variable $ext in /www/wwwroot/gkfeed.com/public_html/wp-content/plugins/show-hidecollapse-expand/bg_show_hide.php on line 281
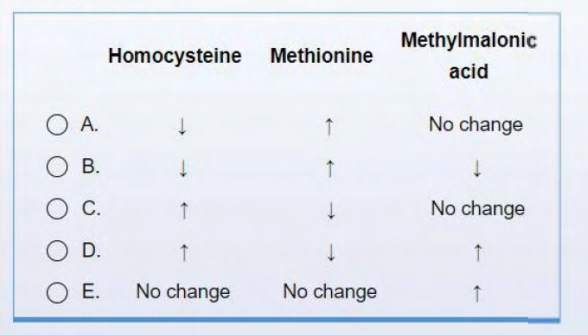
4. A 20-year-old woman comes to the clinic for evaluation of fatigue that has progressively worsened over the past month. The patient was recently diagnosed with celiac disease, but she has not strictly adhered to a gluten-free diet. Laboratory evaluation reveals macrocytic anemia with a low folate level but normal vitamin 8 12 level. Oral folic acid is prescribed. Which of the following biochemical changes is most likely to occur in this patient after starting treatment?
5. A 52-year-old man is being evaluated in the emergency department for abdominal pain associated with watery diarrhea. His symptoms have been progressive over the last month. He says that he is depressed and often has difficulty remembering things. The patient has a 20-year history of alcohol use disorder. On examination, he appears disheveled. A pigmented scaly skin rash is present in the malar distribution of his face, neck, and back of his hands. The rash has been present for several months and worsens on exposure to sunlight. It is determined that the patient’s symptoms are secondary to lack of a specific nutrient. Which of the following enzymes is most likely to be directly affected by this patient’s nutrient deficiency?
A. Citrate synthase
B. Hexokinase
C. lsocitrate dehydrogenase
D. Phosphoglycerate kinase
E. Succinate dehydrogenase
6. Biologists investigating the morphologic changes associated with reversible cellular injury perform a procedure on anesthetized mice to assess the effects of transient hepatic ischemia. During the experiment, they clamp the hepatic artery and obtain liver biopsy samples at varying intervals. The samples are then examined by electron microscopy. Cells that are exposed to longer ischemic periods are found to have reduced numbers of ribosomes attached to the endoplasmic reticulum. This structural change is most likely to impair which of the following cellular functions?
A. ATP production
B. Drug detoxification
C. Synthesis of cell membrane proteins
D. Synthesis of cytosolic proteins
E. Synthesis of steroid hormones
Warning: Undefined variable $in_same_cat in /www/wwwroot/gkfeed.com/public_html/wp-content/plugins/EXP.GKFEED.COM/function.php on line 27
Warning: Undefined variable $excluded_categories in /www/wwwroot/gkfeed.com/public_html/wp-content/plugins/EXP.GKFEED.COM/function.php on line 27