Warning: Undefined variable $ext in /www/wwwroot/gkfeed.com/public_html/wp-content/plugins/show-hidecollapse-expand/bg_show_hide.php on line 281
Warning: Undefined variable $ext in /www/wwwroot/gkfeed.com/public_html/wp-content/plugins/show-hidecollapse-expand/bg_show_hide.php on line 281
Warning: Undefined variable $ext in /www/wwwroot/gkfeed.com/public_html/wp-content/plugins/show-hidecollapse-expand/bg_show_hide.php on line 281
7. Biochemists working for a national endocrinology institute are investigating the specifics underlying glucose transport across adipose cell membranes. One of their experiments shows that, in the presence of insulin, D-glucose transport across the plasma membrane of adipocytes is much faster than L-glucose transport. Which of the following transport processes best describes the mechanism for glucose entry into these cells?
A. Simple diffusion
B. Receptor-mediated endocytosis
C. Carrier-mediated transport
D. Primary active transport
E. Co-transport
8. Researchers lyse human cel ls and isolate a specific messenger RNA template using gel electrophoresis. Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction is then used to synthesize complementary DNA (cDNA) from the RNA template. Next, the cDNA is modified into an expression vector containing an optimized bacterial promoter, ribosomal binding site, and terminator sequence. After insertion of the vector into appropriate bacterial hosts, the transformed bacteria are cultured in a bioreactor and produce large quantities of a protein containing a domain that binds to a specific DNA sequence. This protein is most likely the receptor for which of the following hormones?
A. Glucagon
B. Growth hormone
C. Insulin
D. Insulin-like growth factor
E. Parathyroid hormone
F. Progesterone
9. Succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) is an enzyme complex located within the inner mitochondrial membrane that catalyzes the oxidation of succinate to fumarate. An experiment is conducted to determine if malate alters the rate
of SDH activity. Reaction velocity is measured with and without a fixed quantity of malate as succinate concentration is gradually increased. Obtained results are shown below.
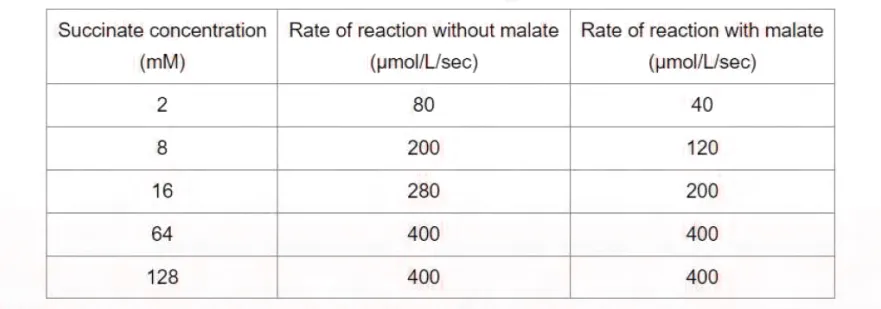
Which of the following is the most accurate statement about malate in this experiment?
A. It alters the maximal velocity of the reaction
B. It binds the enzyme at a different site than succinate
C. It covalently binds the enzyme
D. It decreases affinity of the enzyme for succinate
E. It is a competitive inhibitor of the enzyme
Warning: Undefined variable $in_same_cat in /www/wwwroot/gkfeed.com/public_html/wp-content/plugins/EXP.GKFEED.COM/function.php on line 27
Warning: Undefined variable $excluded_categories in /www/wwwroot/gkfeed.com/public_html/wp-content/plugins/EXP.GKFEED.COM/function.php on line 27