Warning: Undefined variable $ext in /www/wwwroot/gkfeed.com/public_html/wp-content/plugins/show-hidecollapse-expand/bg_show_hide.php on line 281
Warning: Undefined variable $ext in /www/wwwroot/gkfeed.com/public_html/wp-content/plugins/show-hidecollapse-expand/bg_show_hide.php on line 281
Warning: Undefined variable $ext in /www/wwwroot/gkfeed.com/public_html/wp-content/plugins/show-hidecollapse-expand/bg_show_hide.php on line 281
4. Nutrition researchers investigating the relationship between fructose consumption and cardiovascular disease conduct a prospective cohort study on a population of randomly selected young adults. Study participants undergo semiannual measurement of waist circumference, blood pressure, and serum cholesterol and triglyceride concentrations. Dietary fructose consumption is assessed through the use of questionnaires and by measuring urinary fructose excretion. A 23-year-old man enrolled in the study is found to excrete large amounts of fructose in his urine compared to other study participants despite maintaining a moderate fructose intake. Further evaluation shows a hereditary defect in fructose metabolism, but he is asymptomatic and has no other medical problems. This patient most likely remains able to metabolize fructose due to the compensatory activity of which of the following enzymes?
A. Aldolase B
B. Aldose reductase
C. Fructokinase
D. Hexokinase
E. UDP-galactose-4-epimerase
5. As part of an experiment, healthy volunteers undergo a 12-hour fast and then drink a solution containing radiolabeled alanine. Consecutive blood samples are drawn every 15 minutes for the next 3 hours. Initial blood samples detect the radiolabeled alanine, but analysis of later samples shows that the radiotracer is present in blood primarily in the form of glucose. Before alanine can be converted to glucose, its amino group is transferred to which of the following?
A. a-Ketoglutarate (61%)
B. L-citrulline (5%)
C. Malate (7%)
D. Citrate (5%)
E. Oxaloacetate (19%)
6. Molecular biologists perform a series of experiments to characterize the electrophysiologic properties of human muscle cells. The resting membrane potential for an isolated muscle cell is determined to be -70 mV. The equilibrium potentials for important ions under normal physiologic conditions are as follows:
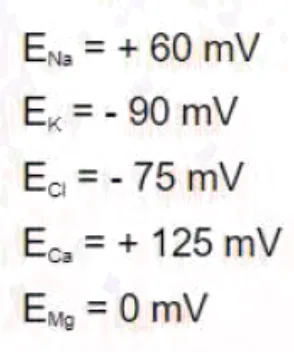
If physiologic conditions are maintained, which of the following ions would most likely flow out of the cell after opening of their respective ion channels?
A. Magnesium and calcium
B. Magnesium and chloride
C. Potassium and chloride
D. Potassium only
E. Sodium and calcium
Warning: Undefined variable $in_same_cat in /www/wwwroot/gkfeed.com/public_html/wp-content/plugins/EXP.GKFEED.COM/function.php on line 27
Warning: Undefined variable $excluded_categories in /www/wwwroot/gkfeed.com/public_html/wp-content/plugins/EXP.GKFEED.COM/function.php on line 27